APA In-Text Citations
Published May 21, 2019. Updated June 21, 2022.
Welcome to our guide on in-text citations! If you’re looking to learn the ins and outs of APA style in-text citations and how to do in-text citations APA, we’ve got you covered in this thorough guide.
The information below follows the 7th edition of the Publication manual of the American Psychological Association.
Here’s a run through of everything this page includes:
- APA Style overview
- In-text citations and why we use them
- Two types of APA in-text citations
- Corresponding entry in reference list
- In-text citations for direct quotes
- Paraphrasing in APA
- How to organize your APA style in-text citation for various scenarios
If you’re simply looking for a quick guide, check out our APA parenthetical citation guide, which serves as a lite-version of this page.
Let’s get started!
What is APA?
This is a term that you might hear your teacher, professor, or librarian throw around a lot. This abbreviation stands for
American
Psychological
Association
This association is kind of a big deal. They do a lot of things related to psychology, but they’re also famous for creating one of the most popular citation styles, APA format. There are other big names on campus, such as MLA format, and Chicago, but this particular style is commonly used by individuals who are writing a science-related paper.
Even if your paper doesn’t necessarily fall into a “science” category, many educators ask their students to cite in this style since it’s so commonly used.
If you’re trying to find information about other commonly used styles, there are more styles on EasyBib.com.
What is an APA In-text Citation?
In plain and simple terms, APA in-text citations are found in the text of a project. Get it? In text. The purpose of an in-text citation in APA is to show the reader, while they’re reading your work, that a piece of information in your project was found elsewhere. They’re placed IN the wording or body of a project, not on the last page; the last page has full references. To learn more about those types of references, check out APA citation.
We’ve all heard about the word plagiarism, and you already know what it means. Simply put, including APA in-text citations are one way to prevent plagiarism.
Here’s what’s included in an APA 7th edition in-text citation:
- Last name(s) of the author(s) or Group name
- Year the source was published
- Page number (if available)
Depending on the number of authors and the source type, some in-text citations look different than others. Read on to learn how to structure an in-text citation for APA. In fact, if you’re looking for an easy route, EasyBib.com has an in-text citation APA generator, which does the work for you. Use our automatic generator to create your full references, and you’ll see an option on the final screen to format your APA in-text citations. An APA in-text citation generator and full reference generator all in one. What could beat that?
Why do we use in-text citations?
When you do a research project, you’re probably going to include facts from websites, databases, books, and other sources. When you add those facts into your project, you must show where those facts came from. It’s the responsible thing to do. It prevents plagiarism. You always give credit to the original author. It’s kind of like thanking them for their contribution to your paper.
Here’s the neat thing about in-text citations. Since they’re IN your project, readers get a quick idea as to where the information you included came from. In-text citations APA are not long and lengthy, like the full references on the APA reference page or APA bibliography. In-text citations are cute, little, and give us the perfect amount of information we need to understand where a fact came from. If you want to get the full information about the source, then you can flip to the back page of the paper, where the full reference is listed. The in-text citation APA style provides us with a tidbit of information. Just enough to glance at it and keep on going with reading the paper.
To recap, in-text citations are great because:
- They credit the original author of a work or information
- They let readers quickly see where the information is coming from
- Including helps make you an ethical writer
If you’re looking to learn more about footnotes in Chicago format, MLA in-text & parenthetical citations, or want to learn how to cite websites in MLA, EasyBib.com has the information you need to be a citing superstar.
Types of APA In-text Citations
Just like there are two days in the weekend, two types of peanut butter (creamy and nutty), and two types of foods we crave (salty and sweet), there are (you guessed it) two types of in-text citations.
The in-text citation APA option you include in your paper depends on how you craft your sentences.
Narrative In-Text APA Citations:
In-text citation APA format, in narrative form, is one that shows the author’s name in the sentence itself.
Narrative In-text APA Citation Example:
Tyson, Strauss, and Gott (2016) encourage the use of simplified terms when it comes to discussing and defining the universe. For example, a small white star is simply called a white dwarf. Keep it short and sweet because the universe is confusing enough (p. 22).
Parenthetical Citations:
This is a type of APA in-text citation where the author’s name(s) are in parentheses, usually at the end of the fact or quote.
Parenthetical Citation Example
Use simplified terms when discussing and defining the universe. For example, a small white star is simply called a white dwarf. Keep it short and sweet because the universe is confusing enough (Tyson, Strauss, & Gott, 2016, p. 22).
As you can see, the type of APA in-text citation you include, whether it’s a narrative one or one in parentheses, depends on how you decide to structure your sentences. It doesn’t matter if you use all narrative, all parentheses, or a mix of both.
What is important is that you’re a responsible researcher and you properly cite your sources!
Remember, most facts, quotes, stats, and copied and pasted information NEED an APA in-text citation next to it.
What’s the only type of information you don’t need to create an in-text citation APA for? Anything that’s common knowledge. For example, paper is made from trees. You and most people already knew that. That’s an example of common knowledge. It’s a piece of information that everyone already knows.
Now, before you simply include the author’s name(s), the date, and the page number in your project and think you’ve covered all your bases, you’re not quite done yet. In-text citations APA are only part of the puzzle.
The other piece of the puzzle is found on the last page of the project: the reference page. That’s where all of the full references are found in their entirety. In-text citations only include the author’s name, year published, and the page number.
The reference page, on the other hand, includes the title of each source, the publishers, the website addresses, and other information. Continue reading to learn why in-text citations and references on the reference page are the perfect match.
Before we continue, MLA works cited pages are very similar to the ones in this style. EasyBib.com has resources for many styles, to help you learn the ins and outs of referencing your work. We even have full pages on grammar topics too, to keep your paper in tip-top shape. Brush up on your noun, conjunction, and interjection skills with our easy-to-follow, comprehensive guides.
Corresponding entry in APA reference list
Would you ever put on one shoe and walk around without the other? Of course not. The same goes with in-text citations and full references. You must include both in your paper. Where there’s one there has to be the other.
Each and every in-text citation APA must have a matching full reference on the reference page (American Psychological Association, p. 262 ).
If you’re wondering why, it’s to allow the reader to get that sneak peek about the source while reading your paper (the APA in-text citation), and then learn all about it on the final page (the reference page). If the reader wants to get their hands on a copy of the sources you used, all of the information they need can be found on the reference page.
Remember those APA style in-text citation examples found above? Let’s take a peek at them again.
Here’s the one with the authors’ names in parentheses:
Use simplified terms when discussing and defining the universe. For example, a small white star is simply called a white dwarf. Keep it short and sweet because the universe is confusing enough (deGrasse, Strauss, & Gott, 2016, p. 22).
Here’s the full reference, which would be found on the final page of the project:
Tyson, N. D., Strauss, M. A., and Gott, J. R. (2016). Welcome to the universe: An astrophysical tour. Princeton University Press.
Notice that in the above in-text citation APA example, the full title of the book, the place the book was published, and the publisher are displayed. If the reader wants to locate the book themselves, all of the information they need is found in the full reference.
One other important thing we’d like to point out is that the same information from the in-text citation APA (Tyson, Strauss, & Gott) matches the first part of the full reference. This is done to allow the reader to easily find the full reference on the final page.
Remember, always include both in-text citations AND full references in your projects.
In the body of projects, in-text citations APA serve an important purpose. They give the reader a snippet of understanding as to the origin of information. It’s just enough information to allow the reader to continue reading the paper in a natural and fluid manner, without having to trip over long, clunky references. If the reader wants to get a detailed understanding of a source, they can flip to the back page, the reference page, to scope out all of the nitty gritty details.
In the next two sections of this page, we’re going to switch gears and share how to properly format direct quotes and paraphrases.
If you’re looking for specific source types, check out APA citation website and APA book citation. These two resources will explain how to format those specific types of references. If you’re stuck and not sure how to start, check out Chapter 10 of the Publication manual for some sample citations.
Direct Quotes in APA
As Drake states in his lyrics, “We don’t like to do too much explaining,” so we’re going to keep this one short and to the point.
“Direct quotes” are a fancy term used for any text that has been copied and pasted into your paper. That Drake quote above is a direct quote.
Direct quotes are any words or sentences copied and pasted into your project, but they don’t necessarily have to be a person’s quote. Anytime you copy and paste text into your assignment, you must include an APA in-text citation next to it. This shows the reader that:
- The information came from another source
- You’re being a responsible researcher and clearly documenting the outside source.
Here are some guidelines to keep in mind when it comes to direct quotes:
- Direct quotes are a solid way to show evidence and prove your point, but use them sparingly. Your paper shouldn’t be riddled with copied and pasted text.
- Put quotation marks around the copied and pasted information. (The exception are APA block quotes, which are direct quotes longer than 40 words and are formatted differently.)
- Always include the page number for direct quotes, if one is available. When formatting APA page numbers for an in-text citation, include p. before the number. Use pp. for a page range.
To create a narrative APA in-text citation, include the author’s last name in the sentence like this:
- As Drake (2013) once said “We don’t like to do too much explaining.”
- In the above APA in-text citation example, the Drake quote was taken from the song, “Started From the Bottom,” in 2013. The title of the source would be included in the reference page.
Or, you include the author’s name in parentheses:
- “We don’t like to do too much explaining” (Drake, 2013).
If you are looking for more examples, go to page 272 of the American Psychological Association’s official Publication manual.
Paraphrasing in APA
We said above that your entire paper shouldn’t have direct quotes everywhere. So, another way to include information from a source is by adding a paraphrase. Simply put, a paraphrase is restated information, but formed using your own words and writing style
APA paraphrases still need an in-text citation since the information was obtained elsewhere. Check out this quote from the song, “For Time,” by Drake:
“I like it when money makes a difference, but don’t make you different.”
To include it in your paper, without using the exact quote, make a paraphrase. Here’s one that would work:
Money has the ability to benefit things in your life, but it’s truly great when it doesn’t cause the person to act differently or change who they are (Drake, 2013).
The above APA in-text citation example is one with Drake’s name in parentheses. If you’d like to include the author’s name narratively, here’s an option:
In Drake’s (2013) lyrics, he shares that money has the ability to benefit things in your life. It’s truly great when it doesn’t cause the person to act differently or change who they are.
It is recommended to include page numbers for paraphrased material, but isn’t required.
Here’s more on paraphrases and direct quotes.
Organizing APA In-text Citations
Ready to learn how to structure your in-text citations? The next section dives deep into developing them and answers “How to do in-text citations APA.” Keep in mind that how each one is formed depends on the number of authors and other factors. All the examples below follow rules laid out in Chapter 8 of the Publication manual.
Even though the structure varies, most in-text citations APA are placed in this manner for narrative in-text citations:
Author’s Last Name (Year) “Quote or Paraphrase” (p. number).
For ones in parentheses, most are placed in this manner:
“Quote” or Paraphrase (Author’s Last Name, Year, p. number).
Notice that whether you choose to include a narrative in-text citation APA or one in parentheses, the author names and the year published are always together. They’re pretty much holding hands. Cute, huh?
Read on to learn the ins and outs of structuring various in-text citations.
Don’t forget, EasyBib.com has an in-text citation APA generator. Wondering what it’s all about? Here’s a quick explanation: We work for you so citing is easy for you. Yep, you read that correctly.
Our tools structure your in-text citations the way they’re supposed to be structured. Use our automatic generator to create your full references, and on the final screen you’ll see the option to create your in-text citations. An APA in-text citation generator that’s easy as pie!
Something else we do for you? We have a plagiarism checker that scans your paper for any instances of accidental copying. We also have tons of grammar pages to keep your page in check. Check out our adverb, preposition, and verb pages.
APA In-Text Citations for Sources with One Author
If your source has one author
If your source has one author, lucky you! Your in-text citation is pretty simple to structure.
Narrative In-text APA Citation:
Author’s Last Name (Year published) are found in the sentence with a “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
Parenthetical APA Citation:
“Direct quote” or Paraphrase (Author’s Last Name, Year published, p. number).
Citing multiple sources by the same author in the same year
You may have a bunch of case studies, articles, or books that you’re referencing, all by the same author. Let’s say you’re analyzing two works by Sigmund Freud, Jokes and Their Relation to the Unconscious and also Fragment of an Analysis of a Case of Hysteria, both of which were published in 1905. Placing (Freud, 1905) in the text would be confusing for the reader. How would the reader determine which source you’re referencing?
If this is the situation you’re in, there’s a pretty simple fix.
Place a lowercase a next to the year in the first source (Freud, 1905a). Place a lowercase b next to the second source (Freud, 1905b). Include those same lowercase letters in the full references on the reference page, like so:
Freud, S. (1905a). Fragment of an analysis of a case of hysteria. https://staferla.free.fr/Freud/Freud%20complete%20Works.pdf
Freud, S. (1905b). Jokes and their relation to the unconscious. https://staferla.free.fr/Freud/Freud%20complete%20Works.pdf
But there’s a catch. When you do this et al. can’t stand for only one author. After all it literally means “and others.” If you have two sources that are identical except for the last author, then you have to write out all the names every time. For example:
Gunderman, Slack, Rausch, and Smith (2017)
Gunderman, Slack, Rausch, and Johnston (2017)
These references are completely the same except for the very last name so you’d have to write all 4 names every time.
If your source has multiple works by the same author
What if you had 2 sources with the same author(s) and same publication year? Lucky for us the solution here is a lot simpler. Just a letter to the publication year!
Gunderman, Slack, and Rausch (2017)
Gunderman, Slack, and Rausch (2017)
Is now:
Gunderman, Slack, and Rausch (2017a)
Gunderman, Slack, and Rausch (2017b)
Just remember to also follow this format in your works cited page even if there is an exact publication date available. See page 267 of your Publication Manual (American Psychological Association, 2020) for a further breakdown.
Need to create an APA in-text citation for a source without an author? How about an APA in-text citation for multiple authors? Continue reading to see the other ways to structure an APA style in-text citation.
APA In-Text Citations for Sources with Multiple Authors
APA in-text citation for sources with two authors
If your source has two authors, place them in the order they appear on the source. Do not place them in alphabetical order.
Narrative In-text APA Citation:
Use the word “and” in between the authors’ names.
1st Author’s Last Name and 2nd Author’s Last Name (Year published) are found somewhere in the sentence with a “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
Parenthetical APA Citation:
If you choose to include both authors’ names in parentheses, use an ampersand in between their names.
“Here is the direct quote” or Here is the paraphrase (1st Author’s Last Name & 2nd Author’s Last name, Year, p. number).
APA in-text citation for sources three or more authors
Only include the first author’s last name and then add ‘et al.’ Et al. is a fancy way of saying “and others” in Latin.
Narrative In-text APA Citation:
1st Author’s Last Name et al. (Year published) are found somewhere in the sentence with a “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
Parenthetical APA Citation:
“Here is the direct quote” or Paraphrase (1st Author’s Last Name et al., Year published, p. number).
If you have author of multiple works (with multiple authors)
Now here is where things can get a tad bit tricky. Sometimes authors with multiple works can cause some confusion in your citations. Generally when that happens you can tell the difference by the publication year, but when you can’t, that’s when you have to list as many authors as necessary to clear up the confusion.
Say you had the two sources below:
Gunderman, Slack, Rausch, and Maule (2017)
Gunderman, Byrnes, Oxner, Wigginton, and Draeger (2017)
Normally, they’d be written as:
Gunderman et al. (2017)
Gunderman et al. (2017)
If you reduced both sources to Gunderman et al. (2017) you wouldn’t be able to tell which source you’re talking about. Instead cite it this way:
Gunderman, Slack, Rausch et al. (2017)
Gunderman, Byrnes, Oxner et al. (2017)
If you’re looking for more information on structuring journal articles, check out our APA journal page.
If you’re looking for a simple solution to referencing multiple authors, EasyBib.com creates in-text citations APA for you! Whether you need to create a reference for one or two authors, or an APA in-text citation for multiple authors, we’ve got you covered!
APA In-text citation no author or date
It’s common to come across sources without any authors. Movies, brochures, website pages often do not have a visible author’s name.
Citing a source with no author
If you find that the source you’re attempting to reference does not have an author, use the first few words from the reference list entry in the APA in-text citation with no author. Most often, it’s the title of the source.
Place the source name in quotation marks if the source is a:
- website page
- article
- chapter
Simply italicize the source name if the source is a:
- Book
- newspaper
- report
- brochure
- Or the full reference starts with italicized information
Remember, you do not have to use the entire title in your in-text citation APA no author. You can use only the first few words from the reference list.
Narrative In-text APA Citation:
“First few words of the webpage, article, or chapter Title” (Year) along with the “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number). OR First few words of book, newspaper, report, or brochure (Year) along with the “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
Parenthetical APA Citation:
“Here is the direct quote” or paraphrase (“Web page, Article, or Chapter Title,” Year, p. number). OR “Here is the direct quote” or paraphrase (Book, Newspaper, Report, or Brochure Title, Year, p. number).
Citing source with no date
No date? No problem! An APA in-text citation no date situation is easier to solve than you think. Only include the author’s name and the page number.
APA in-text citation no date example:
(Foster, p. 35).
Additional APA In-Text Citation Examples
Source by a group, organization, company, or government agency
There are two types of groups: Ones that are abbreviated often and ones that are not abbreviated.
For example, think about these two citation style types: APA and Chicago. One is abbreviated (for the American Psychological Association) and the other is usually written as is (Chicago style).
Abbreviated groups
If the company is often abbreviated, in the first mention in text, display the full name and the abbreviation. In the second and any other subsequent mentions, only use the abbreviation.
Narrative In-text APA Citation:
1st mention:
Full Company’s Name (Abbreviation, Year) with the “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
2nd mention:
Company Abbrev. (Year) “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
Parenthetical APA Citation:
1st mention:
“Direct quote” or paraphrase (Full Company’s Name [Abbreviation], Year, p. number).
2nd mention:
“Direct quote” or paraphrase (Abbreviation, Year, p. number).
Non-abbreviated groups
Always include the full group, company, or organization’s name in each and every mention in text.
Narrative In-text APA Citation:
Full Name of Group (Year) with the “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
Parenthetical APA Citation:
“Direct quote” or paraphrase (Full Name of Group, Year, p. number).
Citing sources with different authors with the same last name
We’re not quite sure how the author of The Baby-Sitters Club (Ann M. Martin) could be used in a paper that’s also referencing the author of Game of Thrones (George R. R. Martin), but hey, it could happen! It’s a Martin party! It’s important to show the reader the difference between the two individuals to prevent any confusion. To differentiate between the two authors in the text, include their first initials.
Example of in-text citation APA:
“Here’s a quote” (A. Martin, Year, p. 6). G. Martin (Year) also states “this direct quote” (p. 45).
As always, keep the author names and the dates directly next to each other. They love being together and it’s a best practice.
Citing multiple sources in the same in-text citation
List sources alphabetically and separate with a semicolon.
Narrative In-text APA Citation:
Be sure to list authors alphabetically.
Johnson (2019), Smith and Adams (2015), and Washington (2017), examined…
Parenthetical APA Citation:
“Direct quote” or Paraphrase (Author 1 Last Name, Year published, p. number if needed; Author 2 Last Name, Year published, p. number if needed)
Parenthetical Citation Examples:
(Johnson et al., 2019; Smith & Adams, 2015; Washington, 2017)
(Honda, 2006, p. 107; Sato, 1980)
If you want to emphasize a source because it is particularly important or relevant, add “see also” before the source’s citation. Think of “see also” as synonymous with “for more information see…”
(Johnson et al., 2019; see also Smith & Adams, 2015; Washington, 2017).
Citing a source within a source
Did you stumble upon the perfect quote that’s quoted in another source? It happens all of the time and it can be a little tricky to figure out how to quote a quote.
The American Psychological Association recommends locating the original quote, if possible. Instead of relying on secondary sources, take the time to locate the original source to make sure the quote is accurate. Finding and reading through the original source also provides you with further information on your research topic!
If finding the original source isn’t possible, due to out of print titles, web pages taken down, or other factors, then it’s okay to quote the secondary source. In your writing, use the phrase “as cited in Secondary Author’s Last name, Year.”
On the reference page, include the reference for the secondary source.
Narrative In-text APA Citation:
As cited in Shapiro’s (2019) article, Carranza stated, “Districts 3 and 15 are showing how we can have the important conversations and take bold action on this issue.”
Parenthetical APA Citation:
Carranza stated, “Districts 3 and 15 are showing how we can have the important conversations and take bold action on this issue” (as cited in Shapiro, 2019).
On the reference page, Shapiro’s article would be referenced in its entirety.
Citing audiovisual material
APA in-text citations for YouTube videos, songs, podcasts, television shows, and other audiovisual materials look a bit different than other types of sources. They include an extra piece of information: a time stamp.
Narrative In-text APA Citation:
Bill Nye (2017) shares that the sun is over four-hundred septillion watts (13:15).
Parenthetical APA Citation:
The sun is over four-hundred septillion watts (Bill Nye, 2017, 13:15).
If you’re still scratching your head, and feeling the urge to type “how to do in-text citations APA” into Google, click here for a website that we dig.
If you’re looking for a quick fix to developing your references, EasyBib.com has you covered! Our tools can help you create an APA in-text citation multiple authors, one author, no authors, plus more!
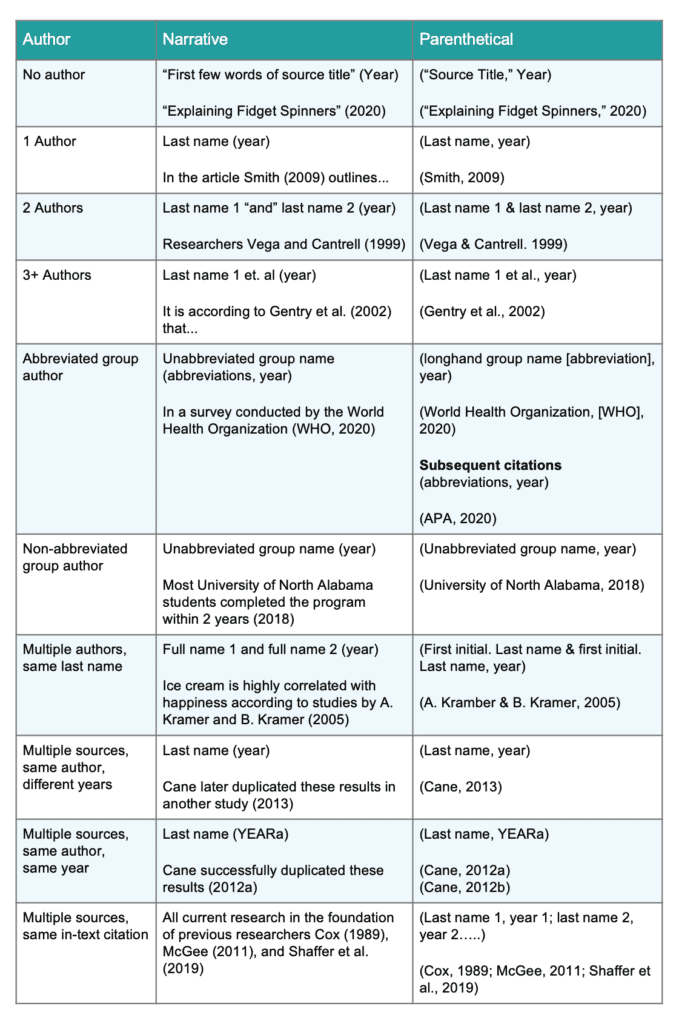
Overview of APA Parenthetical Citations for Websites
Here’s a quick overview of how to create an in-text citation for websites. Notice that since these are for online sources, the in-text citation has no page number.
| Author | Narrative | Parenthetical |
|---|---|---|
| No author | “First few words of source title” (Year)
“Explaining Fidget Spinners” (2020) |
(“Source Title,” Year)
(“Explaining Fidget Spinners,” 2020) |
| 1 Author | Last name (year)
In the article Smith (2009) outlines… |
(Last name, year)
(Smith, 2009) |
| 2 Authors | Last name 1 “and” last name 2 (year)
Researchers Vega and Cantrell (1999) |
(Last name 1 & last name 2, year)
(Vega & Cantrell, 1999) |
| 3+ Authors | Last name 1 et. al (year)
It is according to Gentry et al. (2002) that… |
(Last name 1 et al., year)
(Gentry et al., 2002) |
| Abbreviated group author | Unabbreviated group name (abbreviations, year)
In a survey conducted by the World Health Organization (WHO, 2020) |
(Longhand group name [abbreviation], year)
(World Health Organization, [WHO], 2020)Subsequent citations |
| Non-abbreviated group author | Unabbreviated group name (year)
Most University of North Alabama students completed the program within 2 years (2018) |
(Unabbreviated group name, year)
(University of North Alabama, 2018) |
| Multiple authors, same last name | Full name 1 and full name 2 (year)
Ice cream is highly correlated with happiness according to studies by A. Kramer and B. Kramer (2005) |
(First initial. Last name & first initial. Last name, year)
(A. Kramer & B. Kramer, 2005) |
| Multiple sources, same author, different years | Last name (year)
Cane later duplicated these results in another study (2013) |
(Last name, year)
(Cane, 2013) |
| Multiple sources, same author, same year | Last name (YEARa)
Cane successfully duplicated these results (2012a) |
(Last name, YEARa)
(Cane, 2012a) |
| Multiple sources, same in-text citation | All current research in the foundation of previous researches Cox (1989), McGee (2011), and Shaffer et al. (2019) | (Last name 1, year 1; last name 2, year 2…..)
(Cox, 1989; McGee 2011; Shaffer et al., 2019) |
Once again, if grammar isn’t your thing, and you’re looking for help related to specific parts of speech, check out our adjective, pronoun, and determiner pages, among many, many others!
Follow our EasyBib Twitter feed to find more citing tips, fun grammar facts, and the latest product updates.
References
American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.) https:doi.org/10.1037/0000165-000
Published May 21, 2019. Updated October 25, 2020.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau. Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and one of the in-house EasyBib librarians. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
- What is the difference between the in-text citation and the reference list entry?
-
An in-text citation is a shortened version of the source being referred to in the paper. As the name implies, it appears in the text of the paper. A reference list entry, on the other hand, details the complete information of the source being cited and is listed at the end of the paper after the main text. An example of an in-text citation and the corresponding reference list entry for a journal article with one author is listed below for your understanding:
In-text citation template and example:
Only the author name and the publication year are used in in-text citations to direct the reader to the corresponding reference list entry.
Narrative
Author Surname (Publication Year)
Elden (2003)
Parenthetical
(Author Surname, Publication Year)
(Elden, 2003)
Reference list entry template and example:
Complete information of the reference is used to guide the reader to locate the source for further reference. In the below template, “F” and “M” are first and middle initials, respectively. #–# denotes the page range.
Surname, F. M. (Publication Year). Title of the article: Subtitle. Journal Title, Volume(Issue), #–#. DOI
Elden, S. (2003). Plague, panopticon, police. Surveillance & Society, 1(3), 240–253. https://doi:10.24908/ss.v1i3.3339
- Do all sources need to be cited in-text when using an author-date citation style in APA?
-
When you use APA style, all sources need to have in-text citations. In-text citations direct a reader to the reference entry to get more information on the source being cited in the text. If an in-text citation is not provided, your reader doesn’t know whether there is a source available in the reference list for the idea or topic being discussed in the text. Even if all the basic elements to cite a source are not available, try to provide an in-text citation with the information you do have. For example, if a source does not have an author, use a shortened version of the title in place of the author in your in-text citation. An example is given below for a parenthetical citation.
Author name available:
(Author Surname, Publication Year, p.# for direct quote)
Author name not available:
(“Title of the Work,” Publication Year, p.# for direct quote)
Therefore, in-text citations are essential to guide a reader to locate the corresponding sources in the reference list for the topics discussed in the text.